|
|
|
|
|
|
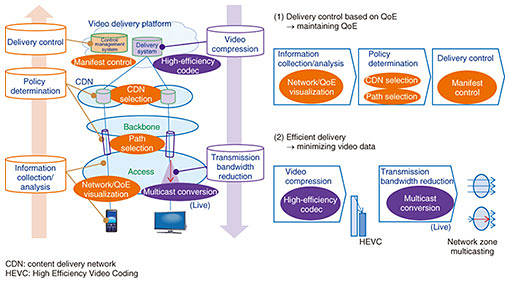
Feature Articles: Network Technology for Digital Society of the Future—Research and Development of Competitive Network Infrastructure Technologies Vol. 17, No. 6, pp. 27–29, June 2019. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr201906fa8 Video Delivery Technology with QoE ControlAbstractThe amount of high-definition content has been increasing significantly lately, and there is also growing demand for video delivery services. This article introduces technology intended to address these issues. It achieves this by delivering high-definition and high-presence video content with high quality in an economical manner by optimizing the server deployment and communication network of content delivery providers and communication providers and by implementing new delivery control techniques. Keywords: CDN, QoE control, multicast conversion 1. IntroductionTo enable a large number of customers to enjoy high-definition video over the network, it is essential that no phenomena occur that can degrade quality within the communication network, or more specifically, that can lower the customer’s quality of experience (QoE). To this end, we propose video delivery technology consisting of two component technologies—technology for controlling QoE and technology for efficiently delivering video data—that are implemented in an end-to-end manner from the video delivery server to the viewing terminal (Fig. 1).
2. Technology for controlling QoEThe technology for controlling QoE consists of three phases: namely, information collection/analysis, policy determination, and delivery control, as summarized below. The information collection/analysis phase uses network/QoE visualization technology to determine whether it is possible to provide QoE that satisfies the customer, and if not, to clarify the phenomena such as network congestion that prevents this. This is accomplished by collecting and analyzing network conditions and server load status from the network as well as information related to customer viewing quality and content from the customer’s viewing terminal. The policy determination phase determines the delivery policy governing the delivery server and content delivery network (CDN) to be selected, the resolution that can be provided, advertising content, and other data in order to provide the appropriate QoE for each customer and gain the customer’s satisfaction. This policy can be set according to the customer’s service, the viewing location, or other factors. The delivery control phase uses the policy established in the policy determination phase to decide on specific delivery conditions such as video resolution and bandwidth that can satisfy the QoE, advertising content, and other information, and which delivery server to use and to perform manifest control for notification to the viewing terminal. Executing these three phases in a linked manner enables the provision of good quality video while avoiding congestion in the network. This technology for controlling QoE was demonstrated at the NTT R&D Forum held in November 2018 in the form of a delivery experiment that connected a server group on the NTT laboratories’ network with a test bed at NTT Communications over the Internet. 3. Technology for efficiently delivering video dataThe technology for efficiently delivering video data encompasses two independent technologies. One is high-efficiency codec technology, which encodes high-definition 4K video in real time based on the HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding) standard. Its proprietary variable-bit-rate control technology can compress video to an amount less than half that of conventional H.264 encoding technology. The other is multicast conversion technology, which converts traffic from unicast to multicast within the network zone while having the delivery provider and viewer use a general-purpose web interface (HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)-based unicast) device. This scheme makes it possible for a delivery provider or network provider to reduce the facility resources needed for data transfer of one item of content by a factor equal to the number of simultaneous viewers. It also enables stable delivery to an individual viewer regardless of the number of simultaneous viewers. In short, the application of these technologies enables the delivery of video at a level of quality that can satisfy many viewers. This technology for efficiently delivering video data was demonstrated at the NTT R&D Forum. 4. Future workIn addition to enhancing the video delivery function in the access network, we plan to develop the all-in-one system architecture from the streaming platform to the viewing terminal for the video distribution business. |