|
|||
|
|
|||
|
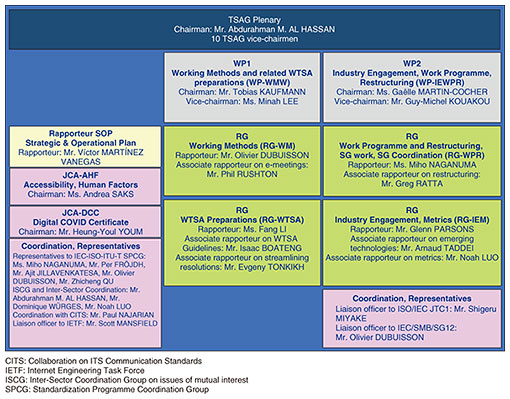
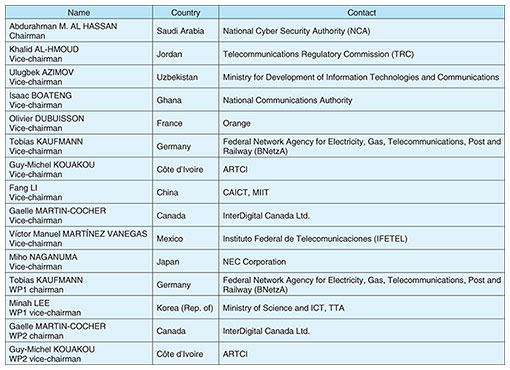
Global Standardization Activities Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 45–49, May 2023. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr202305gls Report of the First ITU-T TSAG Meeting for the 2022–2024 Study PeriodAbstractThe first Telecommunication Standardization Advisory Group (TSAG) meeting for the 2022–2024 study period of the International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) was held from 12 to 16 December 2022 in a hybrid format at ITU Headquarters in Geneva and online. The main outcomes of this TSAG meeting, including the establishment of a Focus Group on Metaverse, are reported in this article. Keywords: ITU-T, TSAG, standardization 1. IntroductionThe Telecommunication Standardization Advisory Group (TSAG) reviews the standardization activities of all Study Groups (SGs) of the International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) and reviews their working methods, meeting rules, and procedures for cooperation with other standardization bodies. On the basis of an analysis of standardization issues to be addressed by ITU-T in the future, TSAG discusses and proposes an SG structure for the next study period to the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA) [1], which is held every four years. The first TSAG meeting for the 2022–2024 study period of ITU-T was held from 12 to 16 December 2022 in a hybrid format at the ITU Headquarters in Geneva and online, with approximately 257 participants from 52 countries. From Japan, the ICT Standardization Division, Global Strategy Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) headed the Japanese delegation, which consisted of 13 in-person participants including Mr. Seizo Onoe, then director-elect of the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau, and participants from companies and organizations (National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), the Telecommunication Technology Committee (TTC), NEC, NTT, NTT DOCOMO, OKI, Hitachi), and 8 remote participants from the MIC, KDDI, NICT, Hitachi, Fujitsu, and the ITU Association of Japan. On the first day of the plenary, the TSAG Management Team proposed a new organizational structure for TSAG meetings, which was approved. The new structure introduces two new Working Parties (WPs), which had not been established before: two Rapporteur Groups (RGs) under WP1, Working Methods (RG-WM) and WTSA Preparations (RG-WTSA), and two RGs under WP2, Working Programme and Restructuring, SG work, SG Coordination (RG-WPR) and Industry Engagement, Metrics (RG-IEM) (Fig. 1). Members of the TSAG Management Team are listed in Table 1. The TSAG chairman is Mr. Abdurahman M. Al Hassan from Saudi Arabia, Ms. Miho Naganuma from NEC was appointed as one of the 10 TSAG vice-chairmen and rapporteur for RG-WPR, and Mr. Shigeru Miyake of Hitachi was agreed to continue as the liaison officer with the International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC) Joint Technical Committee 1 (JTC1).
2. Establishment of new Focus Groups and Joint Coordination Activities2.1 Proposal for a new Focus Group on MetaverseWhen the Focus Group (FG) on Metaverse (FG-MV) was proposed by ITU-T SG16 (Multimedia), a key point for discussion was which organization should be the parent SG. Establishing an ad hoc group (AHG) for creating Terms of Reference (ToR) was proposed on the first day of the plenary and Ms. Gaelle Martin-Cocher (Canada), vice-chairman of TSAG, was elected as the AHG leader. FG-MV was agreed in the plenary to be newly established under TSAG. Regarding the opinion that the term metaverse should not be used from a trademark point of view, the ITU legal department was consulted, and it was confirmed that there was no problem as it is not about selling a product. 2.2 Establishment of Joint Coordination Activity on Machine Learning (ITU-T JCA-ML)The request was made by a liaison from SG13 (Next Generation Networks) and was endorsed on the first day of the plenary because of the wide range of issues related to ML among the SGs. The need for collaboration with ISO/IEC and other standards developing organizations (SDOs) dealing with similar ML-related standardization was noted to avoid duplication of efforts. 2.3 Establishment of JCA on Quantum Key Distribution Network (JCA-QKDN)The FG on Quantum Information Technology for Networks (FG-QIT4N) ended its activities in 2022. The establishment of this JCA was proposed by China and approved because the issues related to QKDN are diverse among the SGs and it is necessary to fulfil a mutual coordination function in a forum such as the JCA. 3. Main results of WP13.1 RG-WMThe RG-WM discusses the work methods in ITU-T and the revision of the ITU-T A-series Recommendations (Organization of the work of ITU-T). At this meeting, the activities of the AHG on Governance and Management of E-meetings (AHG-GME), chaired by Mr. Phil Rushton (UK), were reported. This AHG has been the most active group since the last TSAG meeting. He reported that the AHG has met four times since the last TSAG meeting and compiled a list of issues and guidelines for holding e-meetings. After reflecting the revised comments from each country in the editing session, the Supplement 4 to ITU-T A-series Recommendations (A. Suppl. 4) “Supplement on guidelines for remote participation” was agreed upon. This meeting also agreed on a proposal from Telecom Italia and others to revise A. Suppl. 2 “Guidelines on interoperability experiments and proof-of-concept events” and discussed the Recommendations on working methods and the future course of action for the supplement documents. 3.2 RG-WTSAThe RG-WTSA discusses the consolidation, simplification, and streamlining of Resolutions for WTSA-24. At this meeting, Canada proposed the creation of a one-pager to help WTSA session chairmen work more efficiently by providing a concise summary and reference at hand of the useful guidance found in the A-series Recommendations and Resolution 1. It is envisioned that the one-pager will be developed as an RG-WTSA guideline under RG-WTSA. The proposal was continued for further discussion, as there were different opinions from each country as to whether it is useful or not necessary. There was also a proposal from Russia for the integration and simplification/streamlining of WTSA and Plenipotentiary Conference (PP) Resolutions, and it was agreed to continue the activities for the integration and simplification/streamlining in accordance with the instructions from PP-22, taking into consideration how it should be achieved. In other discussions, it was agreed to develop guidance on “Principles for Reviewing WTSA Resolutions” and guidelines for the preparation of WTSA resolutions. 4. Main results of WP24.1 RG-WPRThe RG-WPR reviews work plans, structures, SG work, and coordination, including the review of activity reports of all SGs, approval of proposed task organization by SGs, coordination of regional groups, coordination among SGs, other SDOs and sectors, and coordination on matters related to SMART (scientific monitoring and reliable telecommunication) submarine cable systems, IMT (International Mobile Telecommunications)-2020, and climate change. In this meeting, the status reports of each SG were introduced and the activities of other SDOs were reported. The action plan for the SG restructuring analysis was discussed with the U.S. participant as the editor, which aims at a thorough review of potential restructuring options for ITU-T on the basis of the empirical analysis, with a view to approving the SG restructuring proposal at WTSA-24. SG restructuring is an important issue that TSAG needs to address. To move forward with the action plan, the definition of key performance indicators (KPIs)/metrics to be collected and analyzed is to be clarified, the priorities of the various KPIs/metrics to be collected and the timing of their implementation are to be identified, and a project plan for conducting the analysis related to SG restructuring (Gantt chart to WTSA-24) was developed and agreed upon. 4.2 RG-IEMThe RG-IEM discusses measures to promote the participation of industry in ITU-T. At this meeting, Canada proposed to add to the ToR of this RG a requirement to promote participation of next-generation personnel from industry in ITU-T and thoroughly review the current industry involvement process, including the current chief experience officer/chief technical officer (CXO/CTO) meeting-coordination process. There were various opinions such as from a legal perspective, and it is important to consider the obligation to participate as well as acquiring rights through participation, and while some said that attending the CXO/CTO meetings was a very positive experience, other commented that there is an inherent problem of not attracting people from industry to ITU-T. Therefore, it is important to solve this fundamental problem so that the participation of future engineers will increase. There was also a proposal from China to send a circular including PP resolutions to organizations that are not members of ITU-T to encourage participation of industry. Russia, Saudi Arabia, and others expressed their agreement with the proposal, but there were some who thought that it was a premature idea, and the proposal was finally included as part of the action plan for the future. 5. Future plansThe 2nd TSAG meeting for this study period is scheduled to be held in Geneva from May 30 to June 2, 2023. Due to the short period until the next WTSA, TSAG meetings are scheduled to be held approximately every six months, with the third TSAG meeting scheduled for January 2024. It was proposed that the final two meetings of TSAG for this study period be held in conjunction with the Inter-regional Meetings. Reference
|
|||