|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Global Standardization Activities Vol. 10, No. 7, pp. 31–35, July 2012. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr201207gls Movement Toward Medical Information Standardization and NTT's Efforts Toward Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE)AbstractIntegrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) is an initiative begun in the USA that has evolved as a guideline for sharing information systems within medical institutions. It is being further expanded to encompass sharing among different medical institutions as electronic health records are implemented at the national level in Europe and in western countries. IHE defines guidelines for efficiently dealing with a variety of standards for health information systems. In recent years, as standard guidelines for cooperation in information exchange between medical institutions of information, awareness of IHE has been increasing. This article describes IHE and NTT's own IHE initiative.
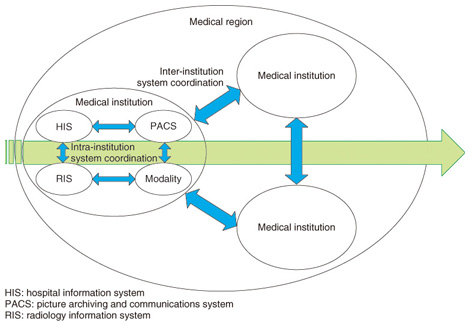
1. IntroductionIntegrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) is an initiative for sharing medical information systems that was created in the USA in 1999 [1], sponsored mainly by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) [2] and the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) [3]. It initially served mainly as a guideline for the sharing of multiple information systems within individual medical institutions (e.g., radiology information and ordering systems). Since the emergence of electronic health records at the national level in European and western countries such as France and the USA, the application of IHE has been further expanded to facilitating sharing among different medical institutions (Fig. 1).
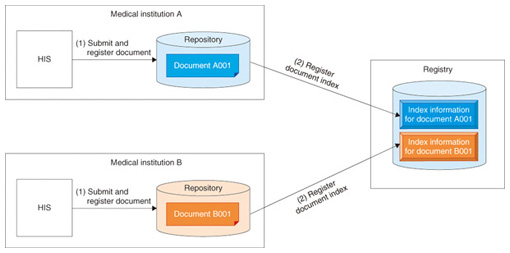
2. Initiative in JapanIHE-J (Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise Japan), which is separate from the American initiative, was established in Japan in 2001 [4] with the initial aim of solving problems related to the transfer of medical images. Japan applied IHE to facilitate connections within medical institutions under the “Project of standardization and verification of regional medical information systems”, a project run by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry from 2006 for three years [5]. In this project, multiple IHE integration profiles such as Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) and Patient Identifier Cross-referencing/Patient Demographics Query (PIX/PDQ) in particular were utilized to create critical paths for a regional health information exchange system for stroke care among multiple health enterprises. 3. National-level initiativesSeveral national projects have recently been started in Japan, including the “Every hospital is my hospital plan” and “Seamless regional medical coordination”. The aims of such initiatives are to promote coordination between hospitals and clinics and coordination between hospitals by sharing diagnoses and laboratory results among multiple medical institutions and ultimately to improve the quality of medical treatment while reducing total costs. For these aims to be accomplished, it is essential to have effective and smooth coordination for information exchange among the medical information systems of multiple medical institutions. The project report for the “Health Information Application Foundation-Building Project”, in which technical requirements and technical specifications for such coordination among multiple medical institutions are defined, includes the proposal to base the foundation on XDS and PIX/PDQ in the IHE integration profile [6]. 4. IHE integration profile used for regional medical coordinationThis section briefly describes the IHE integration profile used in regional medical coordination. 4.1 XDSXDS is an integration profile used to share medical documents among medical institutions [7]. It consists of a document registry and document repository, which store original documents and index information from them, respectively. 4.1.1 Procedural flow of XDSThe procedural flow of cross-enterprise document sharing from a private physician’s office to regional hospitals is as follows (Fig. 2).
(1) Document submission and registration: The original document is registered in the repository of the private physician’s office. (2) Document index registration: The document index is then registered in the registry. The following index information can be registered.
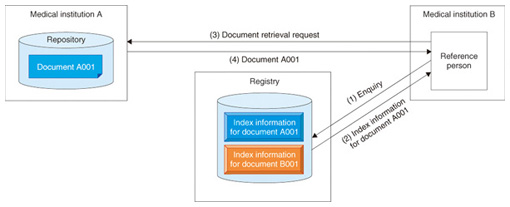
Since the registry must be shared by regional health enterprises, there is one registry for each region. 4.1.2 Procedural flow for document browsingThe procedural flow for inter-medical-institution browsing of registered documents consists of document enquiry and retrieval (Fig. 3).
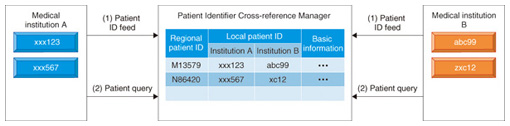
4.2 PIX/PDQWhen XDS is performed as described above, the integration profile for sharing patient information among regional medical institutions is PIX/PDQ [8]. The sharing of patient information is done in the manner described below (Fig. 4).
(1) Registration and renewal of patients’ basic information: Patients’ basic information (regional patient ID, hospital patient ID, patient name, and other information). (2) Enquiry about patients’ basic information: A search of registered patients’ basic information is conducted. As search criteria, the regional patient ID or the patient’s name and date of birth can be entered. 5. NTT’s initiativeSince 2008, NTT has been developing a foundation for information sharing with the purpose of circulating medical information safely and faithfully and has applied it through a company to a project verifying the application of this health information foundation. In 2011, on the basis of the abovementioned circumstances regarding IHE, NTT implemented integration profiles such as XDS and PIX/PDQ in this foundation. Integration profiles such as XDR (Cross-Enterprise Document Reliable) and XDM (Cross-Enterprise Media Interchange) are designated as systems for information sharing among medical institutions and industries [9]. These systems are used to perform information sharing safely even in environments in which registry and repository (explained above as infrastructures for inter-enterprise information sharing) cannot be implemented. XDR is a system used to conduct one-on-one document sharing online, while XDM is a system that uses various media for document sharing. We are actively implementing these systems and additionally verifying connectivity with other companies. 6. Future directionsNTT will closely monitor the movement towards medical information standardization, as with IHE, and continue research and development for promoting regional medical treatments and improving medical treatment quality. References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||