|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
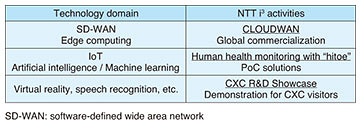
Feature Articles: Global Research and Development Activities by the NTT Group Vol. 16, No. 10, pp. 34–38, Oct. 2018. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr201810fa6 CLOUDWAN: NTT i3 Software-defined Wide Area Network Solution for Edge ComputingAbstractSince its establishment in 2013, NTT Innovation Institute, Inc. (NTT i3) has been developing technologies in the fields of cloud computing and security. Today, technology trends are entering a new stage with the advent of software-defined networking, Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence. This article introduces CLOUDWAN as a software-defined wide area network solution developed by NTT i3. CLOUDWAN provides functions for not only virtual private networks and network functions virtualization but also an edge computing solution through an application delivery function targeting CLOUDWAN’s terminal devices at customer premises. Keywords: edge computing, SD-WAN, IoT 1. IntroductionNTT Innovation Institute, Inc. (NTT i3) was established in 2013 as a sister company to the research laboratories of NTT (holding company). Located in Silicon Valley on the west coast of the United States, it is an applied research and development (R&D) center that aims to contribute to the creation of new business for the NTT Group’s global operation companies. Since its founding, NTT i3 has been targeting cloud computing and security as fields for technology development, and it has been developing products in those fields using in-house or Silicon Valley-developed technologies as well as contributing to open source communities. It has also been introducing NTT Group efforts in innovation to customers (global firms) at its Customer Experience Center (CXC) and providing proof of concept (PoC) activities geared to solving customer problems. Today, five years after its establishment, NTT i3 has come to focus its efforts on new technology fields including software-defined networking, machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and edge computing. Moreover, wireless access technology is progressing rapidly toward the fifth-generation (5G) mobile communications. Thus, technology development in the fields targeted by NTT i3 must correspond to this trend. In addition to technology and product development, NTT i3 is providing PoC solutions in human monitoring for the sports field and manufacturing sector such as the automotive industry. These solutions are being presented as PoC activities using R&D technologies such as “hitoe” (functional wearable material) and machine learning analysis. NTT i3 has also been introducing R&D technologies as its R&D Showcase to visitors since 2017 to obtain feedback from customers in order to improve the future technology development of the NTT laboratories and NTT operating companies (Table 1).
This article introduces CLOUDWAN, a state-of-the-art software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) solution launched by NTT i3 as the result of its technology and product development. SD-WAN is a field that has recently attracted attention as a new trend in network services, and this commercial SD-WAN solution was launched in South Africa and Japan in 2017. One of CLOUDWAN’s advantages is its proprietary edge computing platform that can add functions by delivering applications to terminal devices. We are proposing this innovative solution to operating companies and customers under today’s strong market competition. 2. Background to edge computing technology in IoT environmentEdge computing is a form of cloud computing technology that enables information processing, data storage, and other functions conventionally carried out closer to the place where users or sensors are, rather than in central datacenters [1, 2]. With edge computing, applications run close to the end users, creating faster responses. Edge computing technology can be expected to enable the provision of a variety of new services such as augmented reality, virtual reality, industrial IoT, smart healthcare, connected cars, and smart cities. In particular, the IoT environment requires processing of streaming data from massive IoT devices, but if such a massive amount of data were to be sent to the cloud side, a large communication bandwidth would be needed, or network delays would occur. In contrast, processing on an edge computing infrastructure close to IoT devices can be expected to reduce such data-capacity and delay issues. 3. CLOUDWAN: from SD-WAN to edge computingFrom early on, NTT i3 has been developing and commercializing software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV) technologies. In 2015, we announced Elastic Service Infrastructure (ESI), an NFV-based infrastructure for enterprise networking, and began to deploy it at datacenters. Then, building upon this achievement, we released CLOUDWAN [3] in 2017 as an SD-WAN solution. Internet Solutions in South Africa and NTT PC Communications in Japan have begun to provide CLOUDWAN as their commercial services, and Hitachi, Ltd. is one of the major customers of CLOUDWAN [4] as well. The number of customer premises using CLOUDWAN continues to increase steadily. In addition to offering virtual private network (VPN) and NFV as standard functions by SD-WAN, CLOUDWAN features an application delivery function for its terminal devices. This means that CLOUDWAN can also be an edge-computing infrastructure in the IoT/AI environment. 4. Issues in service delivery and operations in IoT environmentEdge computing is the new horizon for IT (information technology) convergence. The network, services, and functions converge into a single capability that can be delivered anytime and anywhere, and can be instantly updated, removed or modified. Delivering services to distributed areas and offices has always been a challenge. As business enterprises have expanded, the network has exploded as well. However, the way to operate the network has not changed. The existing approach of making the manual task of operating and managing such infrastructure is nearly impossible, as locations and services remain distant and remote. CLOUDWAN is a single solution delivering all the components needed for the journey to edge computing:
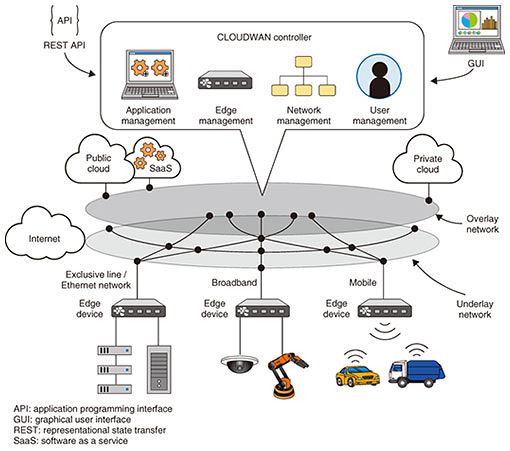
These functions provide uniform management of networks, services, and applications, making it possible to deploy them anytime and anywhere and to perform updates and deletions quickly. 5. Overview of CLOUDWAN functionsThe CLOUDWAN functions are summarized below (Fig. 1).
(1) Edge device Terminal equipment installed on the customer’s premises. The hardware of a terminal under CLOUDWAN is also called a white box, which is hardware equivalent to an ordinary computer server. Loading an edge device with CLOUDWAN operating software gives the terminal a variety of functions. (2) Underlay network The existing legacy network (physical network) for performing simple transmission operations. Here, edge-device networks are set up according to the hardware implemented on edge devices. Physically, this includes Ethernet, LTE (Long-Term Evolution), and Wi-Fi networks with connections made via MPLS (multiprotocol label switching), the Internet, mobile communications, and other means. (3) Overlay network A single, unified network that performs integrated virtual management of the underlay network. Various processes and functions can be performed on this network, which can also be used to connect private and public clouds, and software as a service (SaaS) functions. (4) CLOUDWAN controller An integrated management function on the cloud providing uniform management of users, networks, devices, and applications. It provides a GUI (graphical user interface) in the form of a single dashboard and simplifies operations management by providing REST APIs (representational state transfer application programming interfaces). The above functions are used to set up VPNs and apply NFV, as well as to enable the delivery of applications as elements of edge computing. They can place both communication functions and applications on individual edge devices. To deliver applications, CLOUDWAN adopts the Docker system, a well-known type of containerization software, and this function enables practically anyone to create applications and provide them through the controller. 6. Use case of CLOUDWAN edge computingA variety of use cases can be envisioned for edge computing such as smart cities, smart homes, and automobile-related mobility. NTT i3 presented an edge computing use case demonstration with CLOUDWAN at NTT R&D Forum 2018 (Japan) and at the Mobile World Congress 2018 (Spain) held in February and March 2018, respectively (Fig. 2).
The scenario of this demonstration was a safe intersection in a smart city. In the demonstration, a CLOUDWAN terminal device installed near an intersection was connected to a camera used for monitoring the intersection. An obstacle detection application that is delivered to the device enables it to determine the presence and position of an obstacle in the intersection. If detected, it informs cars entering the intersection of the position of the obstacle and instructs the cars to avoid it. Such a safety solution requires prompt action, so a short delay is directly related to ensuring safety. Consequently, if data processing here were to rely on a public cloud on the Internet, the delay would be longer, and notification of the obstacle might arrive too late for the car to take appropriate action. The edge computing solution is desirable in such a case. 7. Future developmentNTT i3 is working on a global rollout of CLOUDWAN, an SD-WAN solution for the IoT and edge computing environment. Going forward, NTT i3 will continue to target cutting-edge technologies with the aim of fostering innovation in NTT Group global operation companies and global firms. References
|
|||||||||