|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
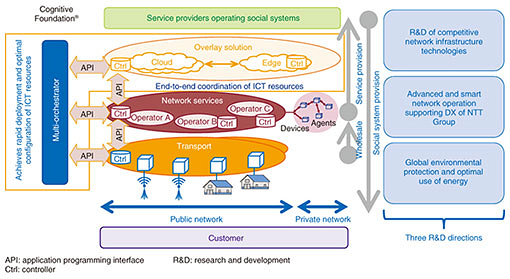
Feature Articles: Network Technology for Digital Society of the Future—Research and Development of Competitive Network Infrastructure Technologies Vol. 17, No. 6, pp. 1–4, June 2019. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr201906fa1 Network Technology Development for Digital Society of the FutureAbstractAs society moves toward digitization, the network supporting a digital society must likewise evolve. NTT has taken up the research and development (R&D) of a network infrastructure called Cognitive Foundation® in order to solve a wide variety of problems in our digital society. This article introduces specific R&D achievements based on the following R&D directions of network technology for the future digital society: (1) R&D of competitive network infrastructure technologies, (2) advanced and smart network operation supporting digital transformation of the NTT Group, and (3) global environmental protection and optimal use of energy. Keywords: digital transformation, cognitive foundation, network technology 1. Network technology required for digital transformationThe Internet of Things (IoT) is advancing rapidly, resulting in numerous benefits. In addition to enabling all sorts of things to be connected to the network and massive quantities of digital data (big data) to be efficiently gathered and stored, the IoT is making it possible to improve business efficiency and productivity through analysis and forecasting using artificial intelligence (AI). At the same time, Japan is faced with serious social problems such as an aging population with a declining birthrate and a shrinking labor force and the need to be continually prepared for natural disasters that can cause massive damage. As a result, expectations are rising for a digital transformation (DX) that can solve such social problems by distributing data across the boundaries separating diverse industries while bringing about important changes in society. As a social infrastructure, the network must be able to quickly and stably provide an optimized network configuration to meet the diverse needs of service operators that manage social systems with a limited amount of information and communication technology (ICT) resources. NTT’s Cognitive Foundation® (Fig. 1) is an overlay networking technology to meet these demands and one of the solutions to achieve DX. This technology covers the network from the cloud to edge computers as virtualized ICT resource groups. It features a multi-orchestration function that acts as a hub for optimally integrating and uniformly managing and operating multiple resources on different layers.
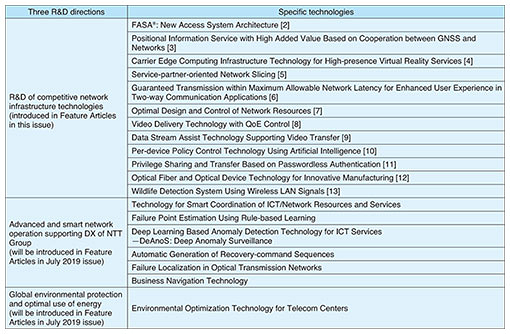
Furthermore, with the progress of DX, it is becoming increasingly necessary for the network to support new digital services such as smart cities, MaaS (Mobility as a Service), and FinTech (financial technology) in addition to the current network services. NTT has established a new research and development (R&D) project to promote the study of a new network infrastructure supporting DX and has begun to discuss use cases with the aim of creating new markets. 2. Three R&D directionsIn this article, we introduce specific achievements of the following R&D directions of network technology for the future digital society: (1) R&D of competitive network infrastructure technologies, (2) advanced and smart network operation supporting the DX of the NTT Group, and (3) global environmental protection and optimal use of energy. 2.1 R&D of competitive network infrastructure technologiesThe first R&D direction is to establish new network infrastructure technologies for increasing communications speed and capacity, expanding connectivity, and lowering costs. The goal is to provide an attractive network for both service providers and service users by increasing the value of our network. These technologies include FASA®* (Flexible Access System Architecture), which converts a portion of the optical access equipment to software in order to switch between a variety of applications including the 5G (fifth-generation mobile communication network) mobile communications standard, and GNSS (global navigation satellite systems), a positioning technology that can greatly improve the accuracy of positioning measurements in unfavorable satellite-signal reception environments such as urban areas while having the potential for use in diverse application services. 2.2 Advanced and smart network operation supporting DX of NTT GroupThe second R&D direction is to establish the automatic network operation technologies in order to respond rapidly to service diversification with as little manual intervention as possible. These technologies can be applied to promote the NTT Group’s DX and to improve the maintenance of social infrastructures. In this way, NTT seeks to contribute to the provision of a network that can respond rapidly to the diverse service demands of various industries through a variety of network operation technologies, including those for achieving sophisticated and efficient operations through the use of AI. These include technology for coordinating services, ICT resources, and network resources across the boundaries between various operators and industries and technology for fault detection, analysis, and recovery to enable rapid restoration of facilities in the event of a problem in the optical transport network. 2.3 Global environmental protection and optimal use of energyThe third R&D direction is to establish resilient network infrastructure technologies that take the global environment into account, including decarbonization, with the aim of achieving the United Nations SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals). NTT is contributing to building a decarbonized society and creating a novel energy distribution business by achieving autonomous energy control centered on drastic energy savings in a cloud-native network and virtualization of the power-supply network. To begin with, we aim to achieve significant energy savings through such initiatives as optimal design of equipment layout in machine rooms. Specific technologies that NTT is pursuing as part of these three R&D directions are listed in Table 1. Some of these technologies are introduced in detail in this issue.
References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||