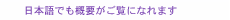|
|||
|
|
|||
|
Global Standardization Activities Vol. 17, No. 12, pp. 35–39, Dec. 2019. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr201912gls Meeting Report of the 31st Asia-Pacific Telecommunity Standardization Program (ASTAP-31) and the Asia-Pacific Telecommunity (APT) Preparatory Meeting for WTSA-20AbstractThe 31st Asia-Pacific Telecommunity Standardization Program (ASTAP-31) was held in Tokyo in June 2019 with the aim of strengthening standardization activities in the information and communication technology field in the Asia-Pacific Telecomunity (APT) and contributing to the regional formulation of international standards. This article reports the results of ASTAP-31 and the status of the first APT preparatory meeting for WTSA (World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly) planned in 2020. Keywords: ASTAP, WTSA, ITU-T 1. The 31st Asia-Pacific Telecommunity Standardization Program (ASTAP) meetingThe Asia-Pacific Telecomunity (APT) was established in 1979 and is an international organization promoting the development of information and communication technology (ICT) in the Asia-Pacific region. It currently has 38 member countries. ASTAP consists of an APT standardization committee that meets every 10 months or so. The 31st ASTAP meeting (ASTAP-31) was held in Tokyo (Akihabara) in June 2019. The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) of Japan hosted this meeting with the support of NTT and other Japanese member companies in order to strengthen cooperation with major Asian countries and coordinate proposals reflecting Japan’s opinions. The meeting had 108 participants from 20 countries. The meeting opened with speeches given by Ms. Areewan Haorangsi, APT Secretary General, and Ms. Yukari Sato, then State Minister of MIC, who spoke on behalf of the host country. 2. First APT preparatory meeting for World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly 2020 (WTSA-20)The first meeting of the APT Preparatory Group for WTSA-20 (APT WTSA-20) was held in conjunction with ASTAP-31. WTSA-20 is one of the most important meetings of the International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T). The purpose is to decide the study group structure of ITU-T, the chair and vice-chair of each study group, and the study theme on the latest technology such as artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) in the study period from 2021 to 2024. In WTSA deliberations, it is common to divide the world into six regions (Asia and the Pacific, the Americas, Europe, Russia (Commonwealth of Independent States), the Arab states, and Africa) and to have common proposals for each region. This is done to improve the efficiency of consensus building. Therefore, the APT WTSA-20 preparatory meetings are crucial for discussing the course of action for WTSA-20. For example, if we try to reflect Japan’s proposals, it will be possible to negotiate with other regions at the regional level by making them an APT common proposals as the Asia-Pacific region. This was the first meeting leading up to WTSA-20, and the selection of the APT WTSA-20 chair, vice-chair, and other officials in charge of the management of the meeting and approval of the meeting structure were made. The structure of the APT WTSA-20 is indicated in Table 1. Mr. Yoichi Maeda, chief executive officer and senior vice president of the Telecommunication Technology Committee (TTC), was elected as chair of APT WTSA-20. In addition, three Working Groups (WGs) were established to discuss ITU-T working methods (WG1), ITU-T work organization (WG2), and regulatory/policy and standardization related issues (WG3). Japan has established a strong support system to reflect its intentions, with three members from Japan selected as the chair or vice-chair of the WGs to promote substantive discussions at meetings. In the future, discussions toward an agreement on the APT common proposals will be held at the preparatory meetings, taking into account the trend of discussions held in ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Advisory Group (TSAG).
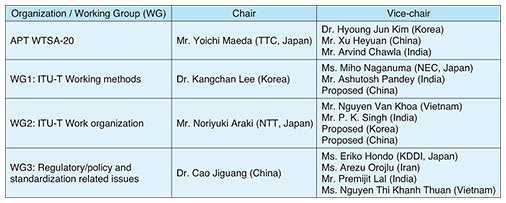
3. Industry workshopsAn industry workshop was held on the afternoon of the first day of the meeting. Seven speakers from four countries gave lectures on disaster response ICT in the first half and smart cities and IoT in the second. The industry workshop programs are listed in Table 2. Promising items for future study in the Expert Groups (EGs) of ASTAP were reported at this workshop.
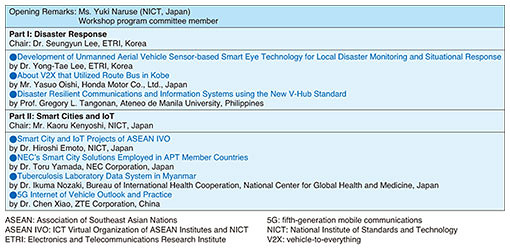
4. Organizational structure of ASTAPThe structure of ASTAP and the respective office bearers are shown in Fig. 1. ASTAP consists of 11 EGs and 3 WGs that organize EGs by technical field. Substantial technical discussions are conducted by each EG, and the outcome documents from each EG are approved by the WG and then finally discussed at the ASTAP Plenary so that efficient discussions can be conducted at each meeting level.
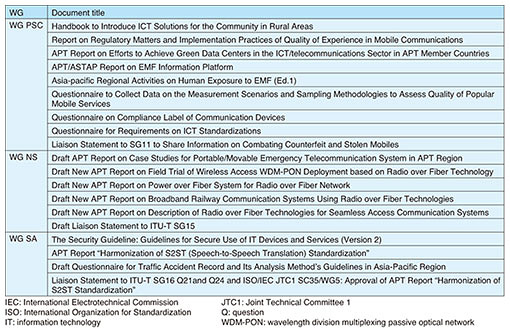
5. Main results of ASTAP-31At the ASTAP meeting, 11 APT reports, 1 guideline document, 4 survey questionnaires, and 3 liaison statements to other standardization bodies were approved. The main output documents are listed in Table 3.
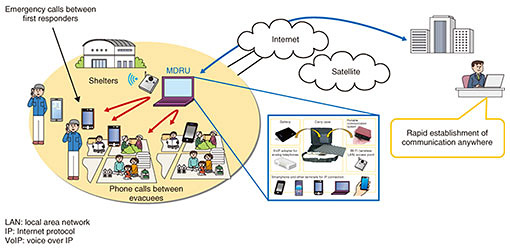
In the EG DRMRS (Disaster Prevention and Recovery System) session, the discussion progressed on the technical report on the use cases of portable emergency communication systems that had been studied based on the proposal from NTT. The use case of portable ICT resource units (MDRU: movable and deployable ICT resource units) [1] during the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake was incorporated into the APT report. The APT report was finally approved by adding the examples of emergency communication systems in China and the Philippines, and the standardization status of disaster response ICT related technology and communication services in other standardization organizations such as ITU (Fig. 2). In the future, it is expected that the use of portable emergency communication systems such as MDRUs will expand in the Asia-Pacific region.
In addition, it was reported that the Information and Communication System using Vehicle during Disaster (V-HUB), of which the APT Recommendation process had been agreed to move forward with at the previous ASTAP-30 meeting, was approved as an APT Recommendation at the 41st APT Management Committee meeting held in October 2018. The voting requirement for an APT Recommendation is that a 25% majority (10 countries) of votes in favor of the Recommendation is received by member countries, and there is no opposition from 2 or more countries. In the EG ITU-T (ITU-T Issues) session, APT member countries, including developing countries, share information and reports on the latest standardization topics, technical trends, and deliberation status in each study group (SG) of the ITU-T. All the SGs of ITU-T gave presentations this time, and APT member countries were able to share information on the current status of each SG and new issues for discussion at WTSA-20. 6. Future plans and issuesASTAP is a meeting to promote standardization activities in the APT region. The ASTAP chairman is from Japan, and the Japanese delegates are office bearers in many of the WGs and EGs. The participants from NTT and Japan also play leading roles in the deliberations of technical documents. Japan is a major country in the APT; and thus, expectations and trust in Japan are extremely high. In a large-scale international standardization conference such as WTSA-20, proposals as a region rather than an individual country are often emphasized, so it is important to always show a presence in the APT region and to deepen cooperation with APT members. For ITU-T, ASTAP as well as APT preparatory meetings will be a valuable opportunity for this purpose. The next APT WTSA-20 preparatory meeting will be held in April 2020, and the 32nd ASTAP meeting will be held in May or June 2020. Reference
|
|||