|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Feature Articles: Media Robotics as the Boundary Connecting Real Space and Cyberspace Vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 27–30, Mar. 2021. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr202103fa5 Affect-perception Control for Enhancing a Sense of Togetherness for Remote SpectatorsAbstractThe COVID-19 pandemic has affected the world of sports and entertainment by expanding the audience for spectator-less sports broadcasts and live-event distribution. In addition to the research NTT Service Evolution Laboratories has been conducting on remote transmission and reproduction of sense-of-presence for event venues, we are promoting research on elemental technology for capturing the emotional movements (affect) of remote viewers to provide what we believe is the emotional feedback needed for such viewers to share a sense of togetherness, interactivity, and excitement as spectators. Keywords: affect, sense of togetherness, enthusiasm 1. BackgroundAs the COVID-19 pandemic is currently restricting personal movement and face-to-face interaction, there has been rapid progress in creating remote forms of various human activities. For sports and entertainment, the broadcasting and live distribution of spectator-less events is increasing. However, it is not yet possible for remote spectators to experience the intensity and extraordinary feeling of being at a stadium or live venue. NTT Service Evolution Laboratories has been conducting research and development (R&D) on technology for sensing the entire space of an event venue and transmitting and reproducing the on-site sense-of-presence and audience enthusiasm to remote live-viewing locations. The technology includes advanced real-time object extraction [1], ultrawide video composition [2], Advanced MMT*1 for synchronous transmission of video and audio [3], and glassless three-dimensional video display that applies the principles of perceptual psychology [4]. However, participation at stadiums and live venues is restricted, and remote sites are not large like live-viewing locations. In a situation where the viewing site is shifting to small, independent locations, such as the home, it is not sufficient to simply convey the enthusiasm and intense moments of the actual site. Instead, a sense of togetherness and interaction among remote spectators can be used to enhance the sense of excitement. We are therefore beginning R&D on affect-perception control for capturing the emotional responses of viewers using simple devices. By establishing elemental technology for that purpose, we intend to enable an experience in which even remote viewers can feel the thrill of watching an event together with many people in a stadium or live venue.
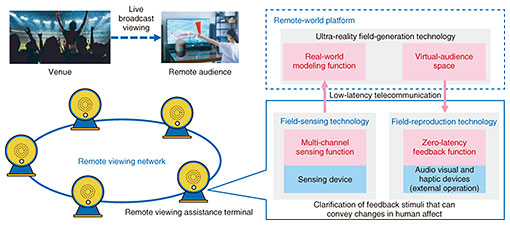
2. Affect-perception controlAffect-perception control can be broadly categorized into three types of technology: field*2-sensing technology for synchronous detection of the remote viewer’s reactions and local situation, ultra-reality field-generation technology for creating a virtual-audience-space model for virtual relocation of a large number of remote viewers from any location in a spatially natural manner, and field-reproduction technology for zero-latency feedback of changes in the affect of other viewers in response to each other’s states in the virtual-audience space (Fig. 1). These technologies are explained in the following sections.
2.1 Field sensingEven when watching the same sports event, some people will follow the movement of a particular player while others are analyzing the overall situation from a wide view and still others are cheering in the audience around them. Thus, what people are paying attention to and the timing of changes in spectator affect differ from person to person. This is also true for other live entertainment events, e.g., when different audience members get excited at different songs or performances. The objective of our research is to achieve real-time sensing, visualization, and quantification of human affect with multi-channel sensing implemented by interworking among multiple sensing devices such as voice-acquisition devices (e.g., smart speakers, television (TV)-mounted cameras), person-sensing devices (e.g., air conditioners), and wearable devices (e.g., smart watches that measure vital signs). Specifically, cameras and motion sensors are used to capture the viewing environment such as the position of the TV, pose of audiences, and line of sight of the viewer. Sensing is used to detect the degree of viewer concentration and which part of the viewing content has the viewer’s interest. Then, the viewing content and changes in the viewer’s movements and voice are analyzed to learn what types of situations are associated with changes in viewer affect. These changes in a viewer’s affect can be measured in more detail by sensing internal body signals, such as body temperature and pulse, at the same time as measuring external changes such as movement. 2.2 Ultra-reality field generationThis technology implements a virtual-audience-space function for real-world modeling that turns the viewer’s environment into a virtual-spatial model and fills the space with many remote viewers in a natural manner. Establishing this technology will make it possible to aggregate the viewer-affect information collected with the technology described in the previous section and categorize viewers by affect to construct an audience space that enhances enthusiasm. It may also be possible to increase the interest of viewers categorized as showing less interest in the content when watching alone by placing them in an audience space with highly enthusiastic viewers. Analysis of sports action and live content to synthesize virtual cheering (fake crowds) according to the exciting parts would make it possible to construct special spaces that create the impression of audiences of tens or even hundreds of thousands cheering in stadiums or event venues that accommodate just a few thousand spectators or even no audience at all. 2.3 Field reproductionThe data for the virtual space described above are combined with information that creates a feeling of the presence of other viewers, such as video, sound, and shadows, to implement a zero-latency feedback function that augments change in viewer affect and enthusiasm. To increase the sense of togetherness among remote viewers by implicitly creating the sense of cheering together side-by-side, we are developing spatial-presentation technology that focuses on touch and other senses in addition to visual and auditory senses. The timing of triggering affect control is also important. Together with technology for bi-directional transfer of a huge amount of sensory data with zero-latency, we are also engaged in R&D on technology for autonomous presentation of information that suggests changes in affect by predicting the next reaction either from changes in viewer affect or context changing in content at the viewer’s location instead of transmitting all the sensory data to each location. To promote R&D on affect-perception control, we constructed an experimental space to verify its effectiveness (Fig. 2). Taking the viewing of a sports event in the living room at home as the use case, we verified the degree of influence on change in viewer affect as well as an optimal sensing and feedback method. We did so by virtually expanding the living room into a virtual connected remote live-viewing venue where multiple spectators gather according to excitement in the game and by presenting performances that produce a reaction by adding effects to video in accordance with the appearance of viewer emotion detected by sensing.
3. Future prospectsFor future work, we will promote R&D for creating new value in the world of remote activities by conducting verification experiments in various real-world situations such as viewing sports events and entertainment distribution with the objective of establishing affect-perception control. References
|
|||||||||||||