|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Global Standardization Activities Vol. 22, No. 10, pp. 66–69, Oct. 2024. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr202410gls Report on the 36th Asia-Pacific Telecommunity Standardization Program Forum (ASTAP-36)AbstractThe 36th Asia-Pacific Telecommunity Standardization Program Forum (ASTAP-36) was held on May 20–24, 2024 in Bangkok, Thailand. More than 150 experts (including 39 remote participants) from 18 nations/regions gathered for four days of standardization discussions and industry workshops. This article outlines the key points of ASTAP-36. Keywords: APT, ASTAP, industry workshop 1. Overview and structure of ASTAPThe international organization Asia-Pacific Telecommunity (APT) was established in 1979 to promote information and communication technology (ICT) development in the Asia-Pacific region. At present, 38 nations and/or regions participate in APT [1]. In 1998, APT established the APT Standardization Program (ASTAP) as a standardization sector meeting. Since its inception, ASTAP has continued to be held once or twice a year. ASTAP’s two main objectives are as follows [2]:
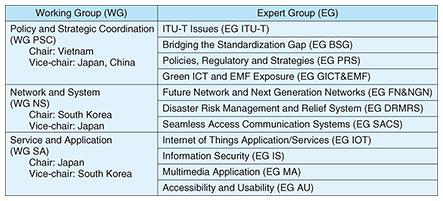
Table 1 shows the meeting structure of ASTAP, which comprises three Working Groups (WGs) and eleven Expert Groups (EGs) reporting to each WG.
1.1 WG Policy and Strategic CoordinationWG Policy and Strategic Coordination (PSC) investigates and shares member policies and strategies with respect to telecommunication technology. It comprises the following four EGs:
1.2 WG Network and SystemWG Network and System (NS) comprises the following three EGs:
1.3 WG Service and ApplicationWG Service and Application (SA) comprises the following four EGs:
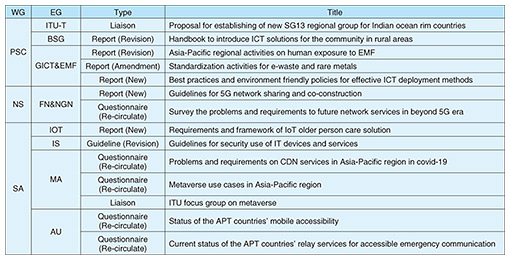
During an opening plenary session held on the first day of the 36th ASTAP Forum (ASTAP-36), all participants shared the program’s overall direction, progress updates, and main objectives for each WG. Individual EG meetings were then held separately over the two days. 2. Major outcomes of ASTAP-36 and action plans for ASTAP-37Table 2 summarizes the major outcomes of ASTAP-36. WG PSC issued a new APT Report titled “Best practices and environment friendly policies for effective ICT deployment methods,” which highlights experiences on environmental protection using ICT technology. WG PSC also revised or amended three existing APT Reports: “Handbook to introduce ICT solutions for the community in rural areas,” “Asia-Pacific regional activities on human exposure to EMF,” and “Standardization activities for e-waste and rare metals,” as scheduled.
WG NS issued one new APT Report titled “Guidelines for 5G network sharing and co-construction.” Chinese and South Korean experts provided extensive comments and proposals to this new report, implying their strong interest in sharing wireless infrastructures to facilitate effective construction and operation. WG SA issued a new APT Report titled “Requirements and framework of IoT older person care solutions.” This WG also accomplished the revision of the existing APT Guideline “Guidelines for security use of IT devices and services.” Table 3 summarizes the main objectives of each WG and EG toward ASTAP-37. Discussions will continue on 21 topics related to new or revised APT Reports/Guidelines. Among these 21 topics, 11 documents are planned to be approved and issued at ASTAP-37. During ASTAP-36, EG FN&NGN agreed to start discussions on a new APT Report titled “Low-altitude network and its key technology” in accordance with the proposal from China and strong support from Vietnam. In this new work item, various applications of social infrastructure management using drones will be investigated, including related key technologies. This new APT Report is expected to be issued at ASTAP-39.
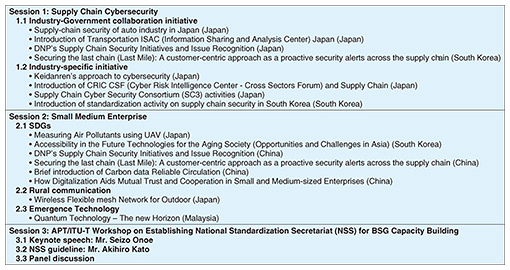
3. Industry workshopASTAP-36 included an industry workshop with its program outlined in Table 4. Three sessions were held consecutively. Session 1 focused on supply chain cybersecurity, showcasing seven experiences from Japan and China that highlighted harmonized activities among industries and governments as well as unique trials in each industry. Session 2 featured nine individual experiences on the effective use of ICT by small and medium enterprises in Japan, China, South Korea, and Malaysia. This session investigated three key aspects: sustainable development goals (SDGs), wireless infrastructure construction in rural areas, and quantum computing. Session 3 was designated as an APT/ITU workshop on establishing national standardization secretariats (NSSs) for BSG capacity building. In this session, Mr. Seizo Onoe, Director of ITU’s Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB), delivered the keynote speech and Mr. Akihiro Kato, Coordination Advisor, ITU TSB, explained the NSS guidelines. A panel discussion followed, enabling the sharing of various opinions and perspectives.
4. Future directionASTAP-37 will be held in 2025, with the exact date and venue yet to be determined. A vice-chair will plan an industry workshop as part of ASTAP-37. References
|
|||||