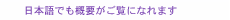|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Global Standardization Activities Vol. 23, No. 1, pp. 56–60, Jan. 2025. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr202501gls TM Forum Latest TrendsAbstractAs we look ahead to sixth-generation mobile communications networks and networks of the future, we share the latest status of the TM Forum discussions on artificial intelligence (AI)-powered automation of operations. There are active discussions on autonomous networks, which is an overall discussion on automation; Open Digital Architecture, which is a business support system/operations support system architecture to achieve automation; and application programming interfaces for business creation in collaboration with various industries such as through B2B2X (business-to-business-to-X). There are also discussions on issues related to the organizations and human resources of telecommunications operators, particularly with a view to applying AI to operations. Keywords: TM Forum, autonomous network, Open Digital Architecture 1. What is the TM Forum?The TM Forum was launched in July 1988 as a non-profit organization to standardize operations to promote interoperability. There are more than 850 member companies, including the world’s leading companies in the telecommunications and information technology (IT) industries. The TM Forum currently has 3 missions, 5 themes, and 20 projects discussing standardization documents, as shown in Fig. 1. The TM Forum is also actively conducting proof of concept (PoC) demonstrations to determine the requirements for standardization through its activities as Catalyst projects.
Three missions:
Five themes:
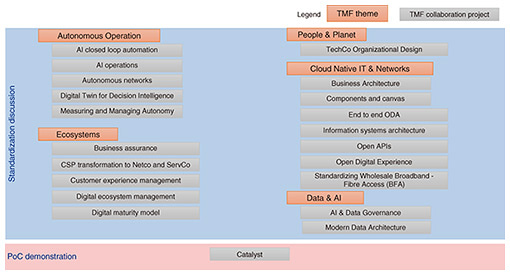
To promote these standards, the TM Forum holds intensive face-to-face discussions once a year and holds workshops and exhibitions once a year in Europe, North America, and Asia. This article reports on trends in autonomous networks, Open Digital Architecture (ODA)/application programming interfaces (APIs), wholesales, people & planet, and AI operations (AIOps). 2. Autonomous networksRegarding autonomous networks, which is a topic on the automation and autonomous operations, discussions are being held in collaboration with other standardization organizations such as 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). The intent model and API, which are the purpose of achieving the overall architecture and automation, level specification of automation, and method of determining the level had been standardized. The architecture of an autonomous network is shown in Fig. 2. In addition to specifying the level of autonomous networks, a method for quantitatively evaluating the level of each company’s operating system using key effectiveness indicators is being specified. With this method, there is a discussion on defining the level of autonomous networks for each network domain such as Internet Protocol or radio access networks.
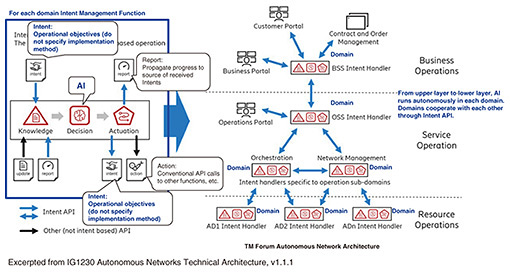
There have been active discussions on automation scenarios using generative AI (Gen AI), and a whitepaper has been created. In this discussion, the creation of a common telecom large language model is also being discussed. Discussions are also underway to clarify the relationship between the architecture and use cases included in the whitepaper. 3. ODA/APIAlong with the development of network software and AI technology, the ODA initiative is underway to transform the business support system/operations support system (BSS/OSS) architecture from a siloed type to an open type and specify specific functions and models as standards (Fig. 3). ODA defines the conventional BSS area as Core Commerce, and the OSS and network areas as Production. ODA has also defined Party Management to address new business models such as B2B2X (business-to-business-to-X). ODA has also defined Engagement Management as a group of functions for a user interface with customers and for flexible cooperation between systems and Intelligence Management as a group of functions for effective use of AI in operations. ODA consists of the Open API that links these functions.
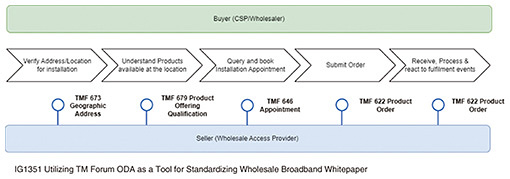
As the ODA study progresses, reference implementations of the functional components that make up ODA are being developed and made available in an environment called ODA Canvas. Figure 3 shows ODA components. The trend at the TM Forum’s Digital Transformation World event shows that the basic idea of ODA has spread to many telecommunications companies. NTT has established guidelines for building future IT systems in compliance with ODA and has obtained the TM Forum’s Running on ODA certification [1]. The TM Forum’s APIs are being considered for expansion to AsyncAPI beyond REST (Representational State Transfer), with fifth-generation guidelines. More than 70 existing Open APIs are also being adapted. There is also active discussion on Domain Context Specialization (DCS) to enable APIs to exchange data not only from existing TM Forum models but also from models defined by other standards developing organizations (SDOs). This DCS allows the TM Forum’s Open APIs to be adapted to specific needs and requirements, resulting in an efficient development process. Therefore, the TM Forum aims to create an open API that is easy to use for non-cloud service provider (CSP) third parties by promoting API collaboration with SDOs. 4. WholesalesWith the expansion of fiber-to-the-x services mainly in Europe, the wholesale business for access services via APIs is accelerating. In Europe and the United States, the operators providing physical networks and the operators providing communication services are often separated. This has led to the consideration of APIs to enable the rapid provision of access services. In accordance with the business processes for providing wholesale services, IG1351 specifies which Open APIs to use (Fig. 4).
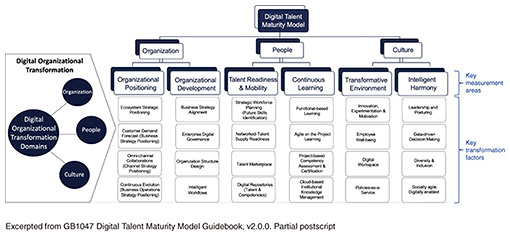
5. People & planetThere are discussions on how organizations and people should transform themselves to become a technology company (TechCo) that actively embraces new technologies such as AI. Specific studies are being conducted to determine which aspects should be considered in the transformation process and index the degree of transformation. For example, the Digital Talent Maturity Model (DTMM) is being considered as a metric to assess the maturity level at which telecom operators are transforming their organization, people, and culture. As shown in Fig. 5, the DTMM focuses on six key measurement areas in three categories: organization, people, and culture, and each measurement area is further divided into key transformation factors. Each transformation factor is divided into five levels of maturity to help identify areas where gaps exist and to plan steps for improvement. To avoid becoming an abstract strategic theory, considerations are being made to clarify the relationship with ODA. Since the discussions are still in their early stages, we will carefully monitor future developments.
6. AIOpsThe TM Forum does not discuss AI algorithms but focuses on developing guidelines and consideration for telecommunications carriers to use AI. Discussions are underway to promote the use of AI by telecommunications carriers by standardizing the lifecycle of models. GB1065 E2E AIOps Lifecycle v1.0.0 breaks down the Design & Development and Maintenance phases of AIOps in detail, enabling the definition of detailed functions by considering the combinations of elements that break down the phases for introducing AI. Discussions on managing and supervising the introduction and operation of AI technologies have become more active as AI & Data Governance. 7. Final thoughtsWe believe that by using the TM Forum, which enables standardization discussions from a business perspective, we can create opportunities for operations technology to be used across a wide range of businesses. NTT laboratories are developing technologies for autonomous automation based on intent and for improving complex and diverse operator operations [2]. By standardizing these technologies, we aim to apply them to a wide range of operational areas. Specifically, we are proposing a contribution to the Intent API (TMF921A Intent Management API Profilev1.1.0) on the basis of the requirements for intent-related technologies, and through demonstrations in the Catalyst project, we aim to promote the spread of our operational technologies for future networks by making them compliant with standards. NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories participated in the Catalyst project “Autonomous Network Hyperloops Phase V,” which consists of 14 companies, and demonstrated the PoC of our intent technology. This project won the Outstanding Catalyst - Beyond Telco award at Digital Transformation World in June 2024. References
|
|||||