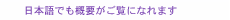|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
Feature Articles: Security R&D for a Better Future Vol. 23, No. 11, pp. 47–53, Nov. 2025. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr202511fa5 Changes in the Environment Surrounding Security R&D and NTT Social Informatics Laboratories’ ChallengesAbstractBased on more than 40 years of the world’s most advanced cryptography research and 20 years of pioneering cybersecurity research, NTT Social Informatics Laboratories is engaged in security research and development (R&D), contributing to the development of society by materializing new activities and businesses that were previously abandoned due to their inability to tolerate risks while contributing to the defense of society. This article introduces our approach to security R&D and the latest priority research themes. Keywords: security, IOWN, AI 1. Security R&D contributing to social developmentThe development of information and communication technology has greatly changed the means of daily communication. Information and communication technologies, such as the Internet, smartphones, and the cloud, have enabled us to transcend distance and time barriers, freely connect with anyone anywhere online, freely access diverse information, and entrust artificial intelligence (AI) to complex tasks that were thought to be possible only by humans. Information and communication technology is bringing about changes in various aspects of society, including family and friend relationships, education and culture, work styles, economic activities, and international relations. The Innovative Optical and Wireless Network (IOWN) and large language model (LLM) tsuzumi, on which NTT is conducting research and development (R&D) and spreading, will become new information and communication technologies that will lead us to a more affluent society. Information and communication technology will transform society with such revolutionary benefits and gradually become indispensable as the technology spreads. However, we need to look at not only the positive aspects of information and communication technology but also the negative aspects. As mentioned above, the seemingly good situation of being able to connect freely online and access diverse information, and being highly supported by AI, may lead to confusion due to invasion of privacy, spread of misinformation and disinformation, work errors due to trust in AI, and deterioration of human relationships and mental health. Misuse, lack of functionality, abuse, and over-reliance on information and communication technology can cause a wide variety of problems. At the same time as the creation of new technologies, it is important to consider and respond to the changes that these technologies bring about in various areas, including society, the environment, the economy, politics, culture, ethics, health, and security. With this philosophy in mind, we are focusing on the positive and negative aspects of the relationship between society and information and communication technology and are engaged in R&D to make evolving information and communication technology, including NTT’s IOWN and tsuzumi, useful for people and not disadvantageous. Our mission is “R&D of information and communication technology that supports social development from the perspective of people,” and our goal is “realization of an affluent society where everyone can live in their own way through the safe and fair use of information” (Fig. 1).
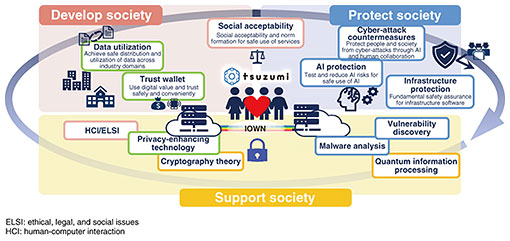
This article presents an overview of our efforts to achieve the above mission and goal from the perspective of security. We have more than 40 years of experience in cryptography research, and cryptography is a fundamental technology to enhance and protect the security of information communications and information management. Over the past 20 years, we have also been focusing on R&D in cybersecurity technologies to address various threats such as unauthorized access, malware infection, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, and phishing. However, I want to emphasize that security technology is not just about protecting. Security technology has the effect of enabling one to do things that one would have previously given up because of unacceptable risk. For example, there are security technologies that lead to the development of society, such as authentication and authorization technologies that enable people who cannot meet in person to verify identity and authority, and secret computing technologies that enable information that is not wanted to be disclosed to others to be used in secret. We are thus anticipating the future and risks posed by information and communication technology, preparing the necessary technologies from the perspective of protecting them, and engaging in R&D to contribute to the development of society by creating various new activities through security. 2. Our environmentAs mentioned earlier, while innovation in information and communication technology contributes greatly to convenience and development, it can also bring about a variety of new problems. I will summarize the current situation and social trends that can lead to such problems. 2.1 Limitations of addressing vulnerabilitiesWith the evolution of software development technology, more and more software is being produced. Naturally, software vulnerabilities (security flaws) disclosed in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) [1], which is operated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the United States, are also increasing at an accelerated pace, reaching a level that is no longer easy to deal with. 2.2 AI/LLM abuse and safetyAlong with the development and spread of AI, cyber-attacks using AI have become apparent, such as the discovery of traces of LLM use to develop attack codes [2]. As AI is incorporated into the basis of various systems, concerns about the safety of AI are rapidly spreading. 2.3 Human cognition exposed to attacksConvenient search services and social media can also be a means to efficiently and accurately investigate target people and organizations online. It has thus become possible to efficiently generate and spread sophisticated misinformation and disinformation that affects people’s cognition, and this has become a factor in fraud and social confusion. 2.4 Interest in and expectations for a decentralized societyWhile the development of cloud services has contributed to society moving online, the risks posed by centralized data management have been highlighted. The European Union is actively working to strengthen individual privacy rights and data sovereignty, and there is growing international interest and expectations for individuals to independently manage and control personal information. 2.5 Advent of quantum computersQuantum computers [3] bring new risks, such as decryption of data, as well as diverse applications. Conventional cryptographic methods are widely used and deeply embedded in important systems that support society, and it is not easy to respond to decryption risks without omission. 2.6 Threats and risks at the national levelAll these threats and risks are spreading not only to individuals and companies but also to national politics, economy, and security, as well as to supply chains across countries. 2.7 Weak security personnel structureThe above situation may further increase the responsibility and importance of security personnel, and their mental and physical burden and tension may exceed the appeal of security work. It may thus become difficult to attract new personnel, making it difficult to maintain the security system. In response to any of these trends, it is necessary to mobilize all efforts not only from the technical side but also from a variety of other aspects to cope with risks. We believe that it is vital to research and develop security technologies from the perspective of creating a better future, rather than focusing solely on reducing such risks. 3. Our effortsHere is an overall map of the major research topics we at NTT Social Informatics Laboratories are focusing on (Fig. 2). This diagram maps our research themes to governance, identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery, which are the categories of security activities defined in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 [4]. On the basis of this framework, we are conducting R&D with the idea that we will prepare the necessary technologies from the viewpoint of protection and at the same time, we will contribute to the development of society by enabling the creation of various new activities through the improved security with these technologies.
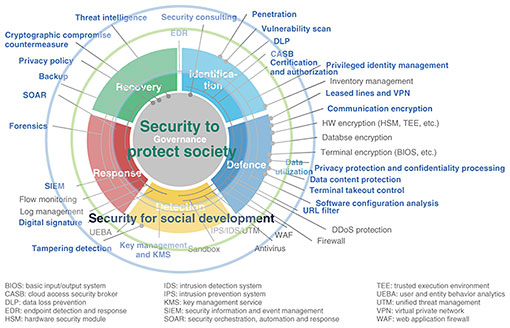
The following sections introduce our research themes and their key points in light of the aforementioned trends. 3.1 Security R&D to protect societyAs mentioned earlier, with the progress in digitalization of society, opportunities for cyber-attacks are increasing, and the damage caused by such attacks is becoming serious. We expect this situation to continue to intensify. To develop even more advanced cyber-attack countermeasures, we are researching innovative cybersecurity technologies that will bring about a game change through collaboration between people and AI (Fig. 3).
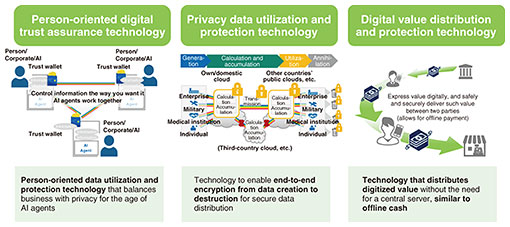
3.1.1 AI security enhancement technologyThis technology enables AI systems to respond to evolving threats. A method for adjusting the AI system (AI model) (alignment) and a method for blocking and controlling inappropriate input/output during the operation of the AI system (guardrail) are effectively combined starting from the safety inspection to enable continuous and timely response. 3.1.2 Vulnerability risk reduction technologyThis technology aims to eliminate the damage caused by exploiting vulnerabilities, from the upstream process of system development to operation. Vulnerability is also a factor in supply chain attacks, and vulnerability countermeasures have become an important issue at the national level since such attacks can bring critical infrastructure to a halt. 3.1.3 Human-centric cybersecurity technologyThis is a technology that evolves security activities from the perspective of the people involved in such activities, centering on collaboration between people and AI. We will create new countermeasure technologies based on the basic premise that both security personnel and end users exposed to threats are people with a mind, which will not only improve security but also improve the experience of security activities. We believe that 20 years of accumulated knowledge and data in the field of cybersecurity will greatly contribute to this research. 3.2 Security R&D for social developmentIn digital transformation, which is expected to be further accelerated due to the evolution of AI, it is important for the owners of diverse digital data in people, organizations, and society to ensure safe distribution and effective use while mutually confirming trust. We are conducting research on digital trust enhancement technologies that enable people to truly rely on information distribution systems and AI. These include technology to control the distribution of digital data throughout its life cycle (generation, distribution, accumulation, utilization, disposal, etc.) on the basis of the wishes of the owners of the digital data and technology to reduce the risk of data leakage and privacy infringement in data processing by enabling different owners of digital data to combine and process them while keeping them encrypted (Fig. 4).
3.2.1 Person-oriented digital trust assurance technologyIn the era of Web3, decentralized identifier/verifiable credential, and AI agents, this technology is a data utilization and protection technology oriented toward individuals that balances business and privacy. Specifically, we grant credentials to people, AI, goods, and data to guarantee and distribute trust. We aim to create technologies that contribute to the foundation of next-generation digital trust in a world where many chains and legacy webs exist. 3.2.2 Privacy data utilization and protection technologyThis technology supports the proper protection and active use of privacy data throughout its creation, use, and destruction, in response to the current situation in which a large amount of privacy data is created daily through various economic and social activities. Even in situations where privacy data spans various organizations, countries, and entities, this technology enables robust data protection and flexible distribution and utilization by creating a virtually integrated end-to-end encryption space on IOWN. 3.2.3 Digital value distribution and protection technologyThis technology distributes digital value such as electronic cash and value information. Like the cash we use offline, we aim to distribute new electronic value without the need for a central server. We are also engaged in R&D in the humanities and social sciences, such as legal systems and privacy. We are thus working to deliver our R&D results to society through both technological development and institutional development. 3.3 Security R&D to underpin next-generation technologiesWe are also engaged in theoretical research that will underpin next-generation technologies 10 to 20 years from now with the aim of continuously creating world-class basic information security technologies. We have world-leading achievements in that a number of our research results have been continuously adopted in prestigious international conferences and journals. We serve as a center of excellence in theoretical research on cryptography and security. 3.3.1 Post-quantum cryptographyWe will drive the safety and security of society by investigating cryptography that cannot be broken by quantum computers (post-quantum cryptography (PQC)). In addition to analyzing the safety and ease of implementation of specific parameters, we aim to establish a cryptographic theory that can achieve both efficiency and composition on the basis of simpler safety assumptions. 3.3.2 Quantum information processing security technologyBy fusing cryptography and quantum information processing, we will promote the creation of pioneering security technologies that can only be created by quantum information processing using physical phenomena unique to quantum environments. 3.3.3 Cryptographic primitive protocol construction theoryOn the basis of cryptographic theory that enables universal and efficient configuration, we will contribute to the timely provision of safe, convenient, and efficient services by providing cryptographic primitive protocols that are optimal for services in socially important and promising fields. 3.3.4 PQC migrationWe are researching and developing technologies to enable us to appropriately and efficiently implement the transition from conventional cryptography to PQC so that people and society will not suffer disadvantages toward the practical application of quantum computers that we will face in 2030. We are also working to standardize the technologies we have created, with the aim of expanding NTT cryptography worldwide. 4. Future developmentsToward the spread of IOWN and the AI-driven society, we will advance security R&D to develop technologies for social development and protection, as well as R&D to underpin next-generation technologies, to make information and communication technology useful for people and not burden with disadvantages. In our R&D activities, we intend to create technologies that are welcomed by society and have real value to people and society while organically linking our research activities and engaging in dialogue and verification with the NTT Group and external partners. We strive to become the source of the advancement in and differentiation of the NTT Group’s security technologies and cooperate with various partners to promote an affluent society where everyone can live in their own way through the safe and fair use of information. References
|
|||||||||