|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
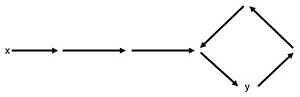
Feature Articles: Challenging the Unknown: Mathematical Research and Its Dreams Vol. 22, No. 9, pp. 26–29, Sept. 2024. https://doi.org/10.53829/ntr202409fa2 Arithmetic Problems in Dynamical SystemsAbstractIn discrete dynamical systems, the ultimate goal is to understand the asymptotic behavior of all points under iterated compositions of a certain transformation (self-map) of a certain space. In arithmetic dynamics, the asymptotic behavior of points with coordinates of arithmetic interest (algebraic numbers or p-adic numbers) is examined. In connection with arithmetic dynamics, some problems are reduced to the determination of rational points on curves. This article introduces the issues in arithmetic dynamics related to these problems. Keywords: number theory, dynamical systems, arithmetic dynamics 1. IntroductionA system in which points move according to a certain rule over time is called a dynamical system. Given a polynomial or a rational map f, we consider the orbit of each point under iterated composition, that is, z Regarding this sequence as a discrete time series, we obtain a dynamical system. The questions of when this sequence diverges to infinity or converges to a certain value are fundamental yet challenging. Arithmetic dynamics studies arithmetic phenomena in such dynamical systems and was established around 2000 by Silverman. Depending on whether the focus is more on number theory or dynamical systems, the nature of the research varies. This article introduces arithmetic dynamics from a number theoretic perspective, particularly problems related to the determination of rational points on curves. Problems from the dynamical-systems perspective are introduced in another article [1] in this issue. One major goal in arithmetic dynamics is to complete the dictionary of analogies between the theory of elliptic curves or their higher-dimensional analogs, Abelian varieties in number theory, and their dynamical system counterparts. Through the dictionary, one often obtains new insights into arithmetic geometry. 2. Morton–Silverman conjectureA torsion point on an elliptic curve is a point that becomes the identity element O under repeated addition. This is equivalent to a point where the orbit under the iterated composition of the doubling map is a finite set. When an elliptic curve is defined over rational numbers, Mazur proved that there are at most 16 such rational points (more precisely, he completely determined the possible group structures) [2]. What about, for example, the iteration of the map z2 on the complex plane? The points, the orbits under z2 of which are finite in the complex domain, are the roots of unity and 0. Among these, the rational points (rational preperiodic points) are only 0, 1, and –1. What about the map Morton–Silverman uniform boundedness conjecture (special case): For any integer d ≥ 2, there exists a constant Nd such that the number of rational preperiodic points of any rational function f of degree d is at most Nd. This conjecture remains largely open even for quadratic polynomials z2 + c (with c a given rational number). It is relatively easy to prove that there are infinitely many cs for which there are rational periodic points z of periods 1, 2, and 3. However, it has been shown that there are no cs for which z2 + c allows rational periodic points of periods 4, 5, or 6 (with the 6-period case requiring the assumption of the Birch–Swinnerton-Dyer (BSD) conjecture) [3–5]. Assuming a generalized abc conjecture, it has been proven that z2 + c does not have rational periodic points of period 4 or higher. One might think of solving the equation fcn(z) = z to find rational periodic points of period n. For n = 4, for example, one would consider the solutions of the polynomial obtained by dividing fc4(z) – z by fc2(z) – z. The situation is similar for general period n. The resulting polynomials are called the n-th dynatomic polynomials. The figure Xndyn defined by these polynomials is a curve, and the problem reduces to determining the rational points on this curve. These problems are familiar to those aware of Fermat’s Last Theorem. In fact, for n = 4, 5, 6, the results are proven using theories developed for determining rational points on specific curves, fully using techniques built up until the solution of Fermat’s Last Theorem. However, it should be noted that the key theory that led to the final proof of Fermat’s Last Theorem is not about determining rational points on specific curves. By using a non-trivial rational solution of Fermat’s Last Theorem, a too-nice elliptic curve called the Frey curve is defined. According to the Taniyama–Shimura conjecture, which is now a theorem, any elliptic curve corresponds to a modular form [6, 7]. However, due to the properties of the original elliptic curve, the corresponding modular form has such too-nice properties that it can be shown not to exist, leading to a contradiction. Therefore, Fermat’s Last Theorem’s non-trivial solution does not exist. While it is natural to explore if this surprising method can be applied to the Morton–Silverman conjecture, no method, such as for defining a Frey curve, has been developed. As mentioned above, Mazur proved that the number of rational torsion points on an elliptic curve is at most 16, but what about the higher-dimensional case, such as Abelian varieties? This problem remains open even for the two-dimensional case. Fakhruddin has shown that this conjecture follows from the Morton–Silverman conjecture, indicating a significance beyond merely following analogies [8]. 3. Dynamical cancellationConsider the following scenario related to the Morton–Silverman conjecture. Let f be a polynomial of degree d. Suppose f has a rational preperiodic point x. Such a point will eventually enter a periodic orbit after certain iterations of f. Suppose it enters a periodic orbit of period 4 at time 3, as illustrated in the orbit diagram (Fig. 1). In this case, let y = f 4(x). Then, x and y collide at time 3. That is, f 2(x) ≠ f 2(y) and f 3(x) = f 3(y). For a fixed rational map f, how many rational pairs (x, y) satisfy f n–1(x) ≠ f n–1(y) and f n(x) = f n(y)? This question is called dynamical cancellation. To answer this, one could examine the existence of solutions (x, y) to the equation
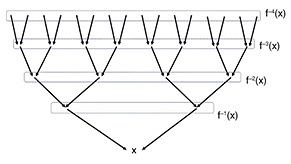
In a different direction from this generalization to higher dimensions, another interesting question is whether the bound on n in dynamical cancellation is independent of f when the degree d is fixed. If this uniform version of dynamical cancellation holds, by considering examples such as those mentioned at the beginning of this section, we can determine the maximum length of the tail of preperiodic orbits, contributing to the Morton–Silverman conjecture. 4. Preimages of 0Returning to the topic of elliptic curves, let us consider the problem of finding torsion points that become O under repeated multiplication by a prime p. How many such torsion points exist? If it can be shown that there are no such points other than O for all but finitely many p, it would yield a result comparable to Mazur’s theorem. Similar considerations are applied to Abelian varieties. In the context of dynamical systems, consider the analogous problem for the map fc(z) = z2 + c. How many pairs of rational numbers (c, z) and positive integers n satisfy fcn(z) = 0? This is the problem of determining rational points on the curve Xnpre defined by fcn(z) = 0. Faber, Hutz, and Stoll have shown, assuming the BSD conjecture, that for n ≥ 4, there are no rational points (c, z) with c ≠ –1, 0. The map sending a point (z, c) on Xnpre to (fc(z), c) on Xn-1predeeply connects these curves, resembling the modular curves describing torsion points on elliptic curves. 5. Arboreal Galois representationsShifting direction from the problem of determining rational points on curves, let us consider problems related to extensions of number fields. As in Kummer’s approach to Fermat’s Last Theorem, the uniqueness of prime factorization becomes a crucial issue when extending the world of numbers (i.e., considering number fields). The extent to which unique factorization fails is described by the quantity called the class number. Computing the class number of a given number field remains a central, challenge in modern number theory. For example, Iwasawa’s theory studying the field extension called In arithmetic dynamics, a similar problem to Iwasawa’s theory arises. Fix an f and rational number x, and consider the tree of points formed by the preimages under iterated composition of f (Fig. 2). The problem of determining the number of rational points in this tree was discussed in section 4, where it was noted that rational points typically disappear early. The field obtained by adding these points to the field of rational numbers is called an iterated Galois extension. How does this extension change as the number of iterations increases? Consider the preimages of 1 under f(z) = zp. This corresponds to considering all p-th roots of unity. Adding these to the field of rational numbers yields a cyclotomic
6. ConclusionI have introduced several number-theoretic problems arising from the iteration of polynomials and rational functions. These problems not only follow the analogy with the theory of elliptic curves and Iwasawa’s theory but also extend techniques from complex dynamics and reveal new arithmetic phenomena. Arithmetic dynamics is still a young field but developing rapidly, involving researchers from various fields such as algebraic geometry, complex dynamics, and arithmetic geometry. I look forward to future research developments. References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||